Two deuterium nuclei, 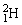 , fuse to produce a helium nucleus,
, fuse to produce a helium nucleus, 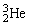 , and a neutron. A neutral deuterium atom has a mass of 2.014102 u; a neutral helium atom has a mass of 3.016030 u; a neutral hydrogen atom has a mass of 1.007825 u; a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 u; and a proton has a mass of 1.007277 u. How much energy is released in the process? 1 u = 931.494 MeV/c2.
, and a neutron. A neutral deuterium atom has a mass of 2.014102 u; a neutral helium atom has a mass of 3.016030 u; a neutral hydrogen atom has a mass of 1.007825 u; a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 u; and a proton has a mass of 1.007277 u. How much energy is released in the process? 1 u = 931.494 MeV/c2.
Definitions:
Basicity
A measure of a substance's ability to donate electrons or accept protons, commonly applied in the context of acids and bases.
Nucleophilic
Characteristic of a chemical species that donates an electron pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in reaction.
t-Butoxide
A strong, non-nucleophilic base, often used in organic synthesis, derived from tertiary butanol.
Ethoxide
An alkoxide derived from ethanol, used as a strong base in organic synthesis, with the formula CH3CH2O-.
Q2: Determine whether the given description corresponds to
Q11: A proton is an example of<br>A)a lepton.<br>B)a
Q17: An engineer is designing a machine
Q33: The good design of experiments includes blinding,
Q34: Discuss the limitations of the Bohr theory.
Q35: The energy gap between the valence and
Q42: The four levels of measurement that are
Q48: The following frequency distribution represents the
Q52: A set of twins, Andrea and Courtney,
Q55: Use technology to develop a simulation of