The position vector of an object of mass 0.50 kg subject to a constant force is given by 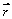 = (at2+bt)
= (at2+bt) 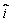 + (ct2+dt)
+ (ct2+dt) 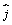 + (et2+ft)
+ (et2+ft) 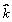 , where a = 2.0 m/s2, b = 3.0 m/s, c = 2.5 m/s2, d = -2.0 m/s, e = 1.0 m/s2, and f = 4.0 m/s. What is the angular momentum of the object about the origin at t = 2.0 s?
, where a = 2.0 m/s2, b = 3.0 m/s, c = 2.5 m/s2, d = -2.0 m/s, e = 1.0 m/s2, and f = 4.0 m/s. What is the angular momentum of the object about the origin at t = 2.0 s?
Definitions:
Physically Separated
Refers to the distinct division or distance between entities or areas, often implying a lack of direct interaction or connection.
Price Discrimination
A pricing strategy where a company charges different prices for the same product or service to different customers, based on the willingness to pay.
Different Prices
The phenomenon where goods or services are sold at varying prices due to factors such as location, demand, or quality.
Pure Monopolist
A single supplier dominates the entire market for a particular good or service, without any competition.
Q11: If the net work done on a
Q19: Refer to Fig. 7-2. What is the
Q30: If you cross a vector with itself,
Q46: If the net work W is done
Q52: A ball is thrown upward with a
Q57: An object floats on a fluid if
Q59: The volume measuring system for a gasoline
Q63: Collisions in which kinetic energy is conserved
Q68: An ideal gas in a container of
Q86: In a section of horizontal pipe with