The position vector of an object of mass 0.50 kg subject to a constant force is given by 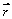 = (at2+bt)
= (at2+bt) 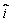 + (ct2+dt)
+ (ct2+dt) 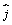 + (et2+ft)
+ (et2+ft) 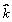 , where a = 2.0 m/s2, b = 3.0 m/s, c = 2.5 m/s2, d = -2.0 m/s, e = 1.0 m/s2, and f = 4.0 m/s. What is the angular momentum of the object about the origin at t = 2.0 s?
, where a = 2.0 m/s2, b = 3.0 m/s, c = 2.5 m/s2, d = -2.0 m/s, e = 1.0 m/s2, and f = 4.0 m/s. What is the angular momentum of the object about the origin at t = 2.0 s?
Definitions:
Marginal Product
The additional output that is produced by employing one more unit of a particular input, while holding other inputs constant.
Fixed Cost
A financial outlay that is unaffected by variations in the production or sales levels of goods and services.
Marginal Cost
The expense associated with creating an extra unit of a product or service.
Total Cost
The complete cost of producing a specific quantity of output, including both fixed and variable costs.
Q10: A 0.400-kg ball approaches a very massive
Q12: A projectile is fired from ground level
Q18: If you push twice as hard against
Q32: The deepest point of the Pacific Ocean
Q36: An object with a mass of 10
Q44: A man lifts a 20.0-kg bucket of
Q58: An inelastic collision of two objects is
Q60: The work done by the centripetal force
Q69: A rod has a length 2.0000 m
Q88: At a fixed depth within a fluid