Vector 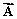 is 75.0 cm long and points at 30° above the positive x axis. Vector
is 75.0 cm long and points at 30° above the positive x axis. Vector 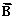 is 25.0 cm long and points along the negative x axis. Vector
is 25.0 cm long and points along the negative x axis. Vector 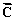 is 40.0 cm long and points at 45° below the negative x axis.
is 40.0 cm long and points at 45° below the negative x axis.
(a) Determine the x and y components of Vector 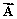 .
.
(b) Determine the x and y components of Vector  .
.
(c) Determine the x and y components of Vector 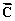 .
.
(d) Determine the sum of these three vectors in terms of components.
(e) Determine the sum of these three vectors in terms of magnitude and direction.
Definitions:
Exports
Goods or services produced in one country and sold to buyers in another country, contributing to a nation's economy.
Nominal Exchange Rate
The speed at which one form of currency can be traded for another.
Currency
A system of money in general use in a particular country or economic context.
Real Exchange Rate
The value of a currency in terms of another currency, adjusted for differences in price levels between countries.
Q12: Find the slope of the line.
Q15: A 900-kg car traveling east at 15.0
Q47: A rocket with a mass of 2.0
Q49: A minimum in the potential energy curve
Q51: The position of an object is given
Q53: Vector <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3817/.jpg" alt="Vector =
Q73: Consider the potential energy U(x) = (1.0
Q77: Potential energy can be defined only for
Q77: A bakery sells three types of
Q81: The velocity of an object as a