The following balance sheets have been prepared on December 31, 2013 for Clarke Corp. and Jensen Inc. 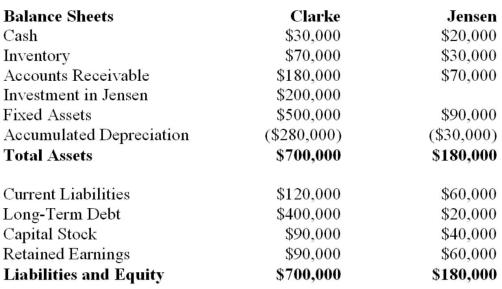 Additional Information: Clarke uses the cost method to account for its 50% interest in Jensen, which it acquired on January 1, 2010. On that date, Jensen's retained earnings were $20,000. The acquisition differential was fully amortized by the end of 2013. Clarke sold Land to Jensen during 2012 and recorded a $15,000 gain on the sale. Clarke is still using this Land. Clarke's December 31, 2013 inventory contained a profit of $10,000 recorded by Jensen. Jensen borrowed $20,000 from Clarke during 2013 interest-free. Jensen has not yet repaid any of its debt to Clarke. Both companies are subject to a tax rate of 20%. Prepare a Consolidated Balance Sheet for Clarke on December 31, 2013 assuming that Clarke's Investment in Jensen is a joint venture investment and is reported using proportionate consolidation.
Additional Information: Clarke uses the cost method to account for its 50% interest in Jensen, which it acquired on January 1, 2010. On that date, Jensen's retained earnings were $20,000. The acquisition differential was fully amortized by the end of 2013. Clarke sold Land to Jensen during 2012 and recorded a $15,000 gain on the sale. Clarke is still using this Land. Clarke's December 31, 2013 inventory contained a profit of $10,000 recorded by Jensen. Jensen borrowed $20,000 from Clarke during 2013 interest-free. Jensen has not yet repaid any of its debt to Clarke. Both companies are subject to a tax rate of 20%. Prepare a Consolidated Balance Sheet for Clarke on December 31, 2013 assuming that Clarke's Investment in Jensen is a joint venture investment and is reported using proportionate consolidation.
Definitions:
Crop-Lien System
A form of credit extended to farmers, typically those who grew cotton, where future crops were used as collateral for loans to purchase supplies and land.
Debt
An obligation or liability to pay or render something to another party, which can be a result of borrowing funds or acquiring goods and services.
Crop-Lien System
A credit system used in the Southern United States after the Civil War, where farmers borrowed against future crop yields, leading to debt and economic dependency.
Natural-Resource Frontier
Areas yet to be explored or developed that are rich in natural resources, such as minerals, forests, and water bodies, offering potential for economic development.
Q1: The procedure used to compute the future
Q4: The capacity concept that allows for normal
Q6: When the acquisition differential is calculated and
Q11: Collins Company, which pays a 10% commission
Q13: Which of the following is not an
Q15: The main idea behind the time value
Q28: On January 1, 2011, Joyce Inc. paid
Q33: The final step in recognizing the completion
Q49: Ting Corp. owns 75% of Won Corp.
Q51: Marshall Welding uses the step-down method of