Ting Corp. owns 75% of Won Corp. and uses the Cost Method to account for its Investment, chapter) for the Year ended December 31, 2013 are shown below: 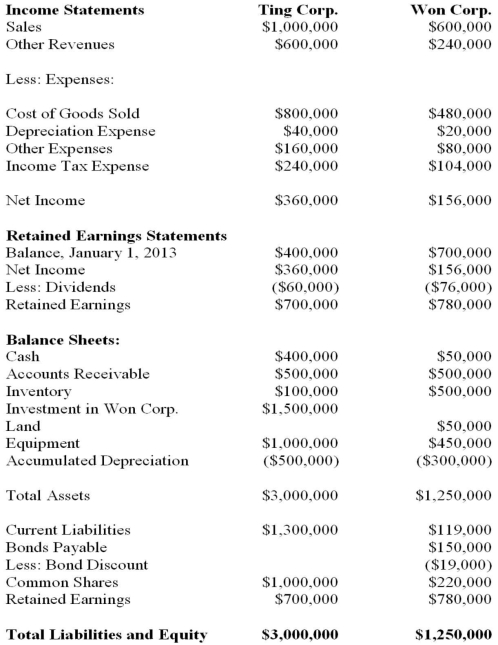 Other Information: ▪Won sold a tract of land to Ting at a profit of $20,000 during 2013. This land is still the property of Ting Corp.
Other Information: ▪Won sold a tract of land to Ting at a profit of $20,000 during 2013. This land is still the property of Ting Corp.
▪On January 1, 2013, Won sold equipment to Ting at a price that was $20,000 lower than its book value. The equipment had a remaining useful life of 5 years from that date.
▪On January 1, 2013, Won's inventories contained items purchased from Ting for $120,000. This entire inventory was sold to outsiders during the year. Also during 2013, Won sold inventory to Ting for $30,000. Half this inventory is still in Ting's warehouse at year end. All sales are priced at a 20% mark-up above cost, regardless of whether the sales are internal or external.
▪Won's Retained Earnings on the date of acquisition amounted to $700,000. There have been no changes to the company's common shares account.
▪Won's book values did not differ materially from its fair values on the date of acquisition with the following exceptions:
▪Inventory had a fair value that was $50,000 higher than its book value.
▪A patent (which had not previously been accounted for) was identified on the acquisition date with an estimated fair value of $20,000. The patent had an estimated useful life of 5 years.
▪There was a goodwill impairment loss of $10,000 during 2013.
▪Both companies are subject to an effective tax rate of 40%.
▪Both companies use straight line amortization exclusively.
▪On January 1, 2013, Ting acquired half of Won's bonds for $60,000.
▪The bonds carry a coupon rate of 10% and mature on January 1, 2033. The initial bond issue took place on January 1, 2013. The total discount on the issue date of the bonds was $20,000.
▪Gains and losses from intercompany bond holdings are to be allocated to the two companies when consolidated statements are prepared. What is the total amount of pre-tax profit from intercompany inventory sales that was realized during 2013?
Definitions:
Organizational Operations
The activities and practices involved in running a business or other organization effectively, including planning, strategy, and execution of various functions.
Mandate
An authoritative command or instruction, often given by voters to elected officials or by higher authorities to subordinates.
Commonsense Notions
Widely held beliefs or judgments that are seen as innate to human cognition without the need for detailed empirical evidence.
Bureaucracies
Organizational structures that manage large-scale public and private operations, characterized by a hierarchical arrangement, a division of labor, and a set of formal rules and procedures.
Q4: Which of the following theories does NOT
Q7: King Corp. owns 80% of Kong Corp.
Q22: How does the accounting for Other Comprehensive
Q35: Do-Good Inc. is a newly formed not-for-profit
Q36: If a business combination occurs and the
Q38: Big Guy Inc. purchased 80% of the
Q54: Which of the following must be possible
Q67: When allocating service department costs, companies should
Q78: Construct a <span class="ql-formula" data-value="90
Q94: A confidence interval with a 95% level