Test a Hypothesis Regarding Three or More Means Using One -Way ANOVA
-An industrial psychologist is investigating the effects of work environment on employee attitudes. A group of 20 recently hired sales trainees were randomly assigned to one of four different "home rooms" - five trainees per room. Each room is identical except for wall color. The four colors used were light green, light blue, gray and red. The psychologist wants to know whether room color has an effect on attitude, and, if so, wants to compare the mean attitudes of the trainees assigned to the four room colors. At the end of the training program, the attitude of each trainee was measured on a 60 -pt. scale (the lower the score, the poorer the attitude) . The data was subjected to a one-way analysis of variance. Give the null hypothesis for the ANOVA F test shown on the printout.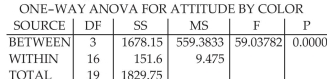
Definitions:
Equilibrium Price
The price at which the quantity of a product offered is equal to the quantity of the product in demand.
Elasticity Coefficient
A measure that quantifies how a change in one economic variable, such as price, affects the quantity demanded or supplied of another variable.
Perfectly Inelastic
A situation in demand or supply in which the quantity demanded or supplied does not change regardless of changes in price.
Quantity Demanded
The specific amount of a good or service consumers are willing to purchase at a given price.
Q19: Is a confidence interval or a prediction
Q30: A medical researcher wishes to try
Q38: When testing <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\mathrm
Q42: The dean of a major university
Q68: Suppose you are using <span
Q70: A gym teacher uses three exercises
Q71: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\mathrm { a } _
Q86: A scientist was studying the effects of
Q129: Given the following five-number summary, find
Q151: For the following data set, approximate