Construct and Interpret Confidence Intervals about the Population Mean Difference of Matched -Pairs Data
-Seven randomly selected plants that bottle the same beverage implemented a time management program in hopes of improving productivity. The average time, in minutes, that it took the companies to produce the same quantity of bottles before and after the program are listed below. Assume the two population distributions are normal. Construct a confidence interval for . Assume that the paired data came from a population that is normally distributed.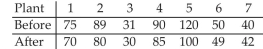
Definitions:
Career Success
The achievement of personal work-related goals and fulfillment in one's professional life over time.
Machiavellians
Machiavellians refer to individuals who exhibit a manipulative personality trait, often using deceit or cunning as a strategy to achieve their goals.
Organizational Politicians
Individuals within an organization who engage in tactical behavior and manipulation to achieve personal or organizational objectives.
Networking
The act of connecting and building relationships with other professionals for the purpose of exchanging information, advice, and support.
Q23: A builder has two crews that
Q45: A recent survey showed that in
Q53: A method currently used by doctors
Q60: Given <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\mathrm {
Q68: A one-sample sign test is a test
Q81: When performing a multiple linear regression,
Q97: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\text { Test the claim
Q115: True or False: Type I and Type
Q131: The following is a sample of
Q147: The top speeds (in mph) for