Given the following null and alternative hypotheses H0 : μ1 ≥ μ2 HA : μ1 < μ2 Together with the following sample information 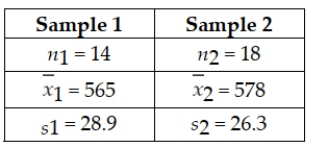 Assuming that the populations are normally distributed with equal variances, test at the 0.10 level of significance whether you would reject the null hypothesis based on the sample information. Use the test statistic approach.
Assuming that the populations are normally distributed with equal variances, test at the 0.10 level of significance whether you would reject the null hypothesis based on the sample information. Use the test statistic approach.
Definitions:
Q15: A walk-in medical clinic believes that arrivals
Q17: State University recently randomly sampled ten students
Q22: An analyst plans to test whether the
Q53: In order to test the difference in
Q54: If a hypothesis test is conducted for
Q87: The prediction interval developed from a simple
Q90: A major manufacturer of home electronics is
Q110: If a simple least squares regression model
Q115: Which of the following statements is true?<br>A)
Q116: Which of the following statements is correct?<br>A)