Find a deterministic finite-state automaton equivalent to the nondeterministic finite-state machine shown. 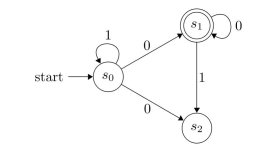
Definitions:
C-Section
A surgical procedure known as cesarean section, used to deliver a baby through an incision in the mother's abdomen and uterus.
Low-Birthweight
Refers to babies born with a weight of less than 2,500 grams (5 pounds, 8 ounces), often associated with developmental or health issues.
Food Insecurity
A condition where individuals or households lack reliable access to sufficient quantities of affordable, nutritious food.
Doula
A trained professional who provides continuous support to a mother before, during, and shortly after childbirth to help her achieve the healthiest, most satisfying experience possible.
Q3: What is the output of the following
Q5: How many ways are there to assign
Q7: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\text { Let } f
Q29: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\left| B ^ { \prime
Q45: Eric is taking MTH 281.
Q53: Determine whether the following argument is
Q66: Suppose A = <span class="ql-formula"
Q91: Show that the premises "Every student in
Q105: Prove or disprove: <span class="ql-formula"
Q146: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\text { The set of