The following is called the Chaos Game. Start with a square ABCD in which A is located at (0,0), B is located at (27,0), C is located at (27,27) , and D is located at (0,27) . Then, roll a fair die. We will say that A is the winner if we roll a 1, B is the winner if we roll a 2, C is the winner if we roll a 3 , and D is the winner if we roll a 4 . If we roll a 5 or 6 , we disregard the roll and roll again. Each roll of the die generates a point inside or on the boundary of the square according to the following rules.
- Start: Roll the die. Mark the winning vertex and call it P1 .
- Step 1: Roll the die again. From P1 move two-thirds of the way straight towards the next winning vertex. Mark this point and call it P2 .
- Steps 2,3, etc.: Continue rolling the die, each time moving to a point two-thirds of the way from the last position to the winning vertex.
The grid below show the square ABCD .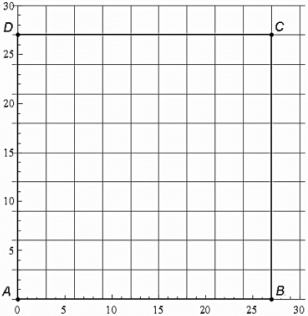
What would be the sequence (1,2,3) was rolled?
Definitions:
Plasma Membrane
This is a protective double lipid layer encasing the cytoplasm of a cell, overseeing the transportation of substances across the cell boundary.
Membrane Potential
The electric potential difference across a cell's plasma membrane, crucial for the transmission of nerve impulses and muscle contraction.
Local Potential
A reversible, localized change in the electrical potential of a neuron's membrane, which can lead to an action potential if a certain threshold is reached.
Depolarization
A reduction in the difference in electric charge across a cell membrane, which is essential for generating action potentials in neurons and muscle cells.
Q4: Suppose a phrase-structure grammar has productions S
Q5: On Valentine's Day you and your date
Q10: After several weeks of compiling data you
Q13: Since 2011, a total of 68 college
Q19: Based on the scenario above, how many
Q28: Refer to the table shown above ;
Q29: Ron , Tim , Sam , and
Q31: Using only the five properties associative laws,
Q36: Consider the weighted graph given below; which
Q43: If T is a binary tree with