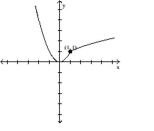
Compare the right-hand and left-hand derivatives to determine whether or not the function is differentiable at the point
whose coordinates are given.
-
Definitions:
Degrees of Freedom
The count of individual values or magnitudes that may be allocated to a statistical distribution without breaking any limitations.
Sample Size
The number of observations or individuals taken from a population to form a sample for the purpose of statistical analysis.
Variance Accounted
A measure of the proportion of the total variance in a dataset that is explained or accounted for by a statistical model or factor.
Correlation
A numerical indicator that reveals the degree to which two factors vary in tandem, showcasing the intensity and orientation of their association.
Q7: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="y = u ( u
Q34: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\text { Determine the values
Q110: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="y=\frac{x^{3}}{x^{2}-25}"><span class="katex"><span class="katex-mathml"><math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><semantics><mrow><mi>y</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><msup><mi>x</mi><mn>3</mn></msup><mrow><msup><mi>x</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mo>−</mo><mn>25</mn></mrow></mfrac></mrow><annotation encoding="application/x-tex">y=\frac{x^{3}}{x^{2}-25}</annotation></semantics></math></span><span
Q140: Maximum<br><img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6591/.jpg" alt=" Maximum
Q231: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="y = \sqrt [ 3
Q271: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="g ( x ) =
Q296: A manufacturer uses raw materials to produce
Q374: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="r = 20 - \theta
Q458: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="y = 2 \sin ^
Q484: Rewrite tan x and use the product