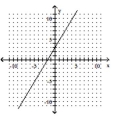
Graph the inverse of the function plotted, on the same set of axes. Use a dashed curve for the inverse.
-
Definitions:
Economies of Scale
Enterprises see cost efficiencies due to their operating scale, with the cost for every unit of output generally declining as the scale enlarges.
Economies of Scale
Describes the cost benefits that companies achieve through their operation size, where the cost for each unit produced typically falls as the scale of operation grows.
Constant Marginal Cost
A situation in which the cost of producing one additional unit of a product remains the same, regardless of the volume produced.
Average Fixed Cost
The cost that a company incurs for fixed resources divided by the quantity of output produced.
Q85: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="y=-f(x)"><span class="katex"><span class="katex-mathml"><math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><semantics><mrow><mi>y</mi><mo>=</mo><mo>−</mo><mi>f</mi><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><mi>x</mi><mo
Q91: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="y = \frac { 8
Q114: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\frac { x ^ {
Q128: The bar graph below shows a
Q137: What is the probability that the
Q177: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\frac { 32 ^ {
Q209: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="5 , - 10,20 ,
Q232: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="3 ^ { 4 }
Q280: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\sum _ { i =
Q387: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\ln \left( 1 + x