Solve Problems Involving Systems Without Unique Solutions
Solve the problem using matrices.
-The figure below shows the intersection of three one-way streets. To keep traffic moving, the number of cars per minute entering an intersection must equal the number of cars leaving that intersection. Set up a
System of equations that keeps traffic moving, and use Gaussian elimination to solve the system. If
Construction limits z to t cars per minute, how many cars per minute must pass through the other
Intersections to keep traffic moving? 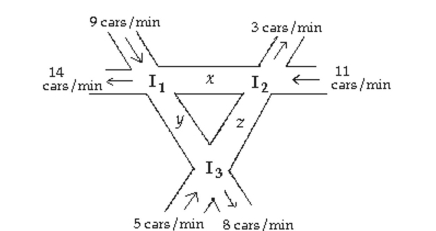
Definitions:
Laissez-Faire Society
A society where transactions between private parties are free from state intervention, including restrictive regulations, taxes, tariffs, and enforced monopolies.
Social Control
Mechanisms, strategies, and processes that regulate individual and group behavior, aiming to maintain conformity and compliance within a society.
Capitalism
An economic system characterized by private or corporate ownership of capital goods, investments determined by private decision, and prices, production, and the distribution of goods that are determined mainly by competition in a free market.
Growth of the State
The process of increase in the size and scope of government activities, often referring to the expansion of its regulatory, taxing, and coercive capacities.
Q12: A traffic engineer is counting the
Q30: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\begin{aligned}x + y + z
Q30: In a student government election, 5 seniors,
Q61: x - y > -2 <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1195/.jpg"
Q75: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="x ^ { 2 }
Q91: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\frac { x - 17
Q133: Use the coding matrix <span
Q185: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\log _ { b }
Q220: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="a _ { n }
Q236: Jarod is having a problem with rabbits