The following MINITAB output presents a multiple regression equatior =b0+b1x1+b2x2+b3x3+b4x4
The regression equation is
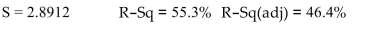
Let be the coefficient Test the hypothesis versus level. What do you conclude?
Definitions:
Gross Profit Margin
A financial metric that represents the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of goods sold, indicating the efficiency of production.
Cost Of Goods Sold
Expenses directly associated with the creation of a company's sold products, including both materials and workforce costs.
Sales
Sales represent the total revenue earned from goods or services sold by a company during a certain period.
Gross Profit Margin
A financial ratio that indicates the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of goods sold, highlighting the efficiency in producing and selling products.
Q9: The amounts 5 and 2 are compared.
Q16: Lindley Corp.'s stock price at the end
Q20: Ratio analysis involves analyzing financial statements in
Q20: A poll was taken of 13,795
Q26: A sample of 6,000 computer monitors
Q28: Wells Water Systems recently reported $8,250 of
Q52: When estimating the cost of equity by
Q61: Using technology, use the Central Limit
Q62: A Karate club consists of 54 persons
Q68: Suppose firms follow similar financing policies, face