The following MINITAB output presents a multiple regression equatior =b0+b1x1+b2x2+b3x3+b4x4
The regression equation is
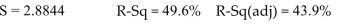
It is desired to drop one of the explanatory variables. Which of the following is the most appropriate action?
Definitions:
Binding Minimum Wage
A government-set minimum wage that is above the equilibrium wage, potentially leading to unemployment because the quantity of labor supplied exceeds the quantity demanded.
Labor Demanded
The total number of workers that employers are willing and able to hire at a given wage rate in a certain period of time.
Labor Supplied
The aggregate amount of hours that employees are prepared and capable of working for a specified rate of pay.
Binding Price Floor
A minimum price set by the government or body above the equilibrium price, leading to excess supply if the market cannot legally adjust to its equilibrium.
Q2: When experimental units are people, they are
Q5: Which of the following statements is CORRECT?<br>A)
Q33: On the balance sheet, total assets must
Q36: The following display from a TI-84
Q40: Fill in the missing value so
Q49: One problem with ratio analysis is that
Q52: The Australian sheep dog is a breed
Q69: The cost of common equity obtained by
Q80: The following normal quantile plots each illustrate
Q81: Quigley Inc. is considering two financial plans