The following MINITAB output presents a multiple regression equation .
The regression equation is
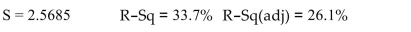
Predict the value of when
Definitions:
Favourable Variances
Differences between actual costs and budgeted costs that result in a better-than-expected financial performance, often indicating cost savings or higher revenues.
Large Variances
Significant differences between planned and actual figures in a budget, project, or any performance measurement, indicating greater deviations from expectations.
Consistent Trends
Patterns or changes in data that continue over a period of time in a similar manner.
Standard Direct Labour Hours
The estimated amount of labor hours required to produce a certain amount of output under normal conditions.
Q7: A poll was taken of 14,537
Q9: In a study of reaction times,
Q12: Which of the following statements is CORRECT?<br>A)
Q21: Following are heights, in inches, for
Q24: One of the primary feeds for
Q37: Find the median of the data
Q55: At an airport, 77% of recent flights
Q68: Rivoli Inc. hired you as a consultant
Q70: The following boxplots each illustrate a sample.
Q89: Funds acquired by the firm through retaining