The following MINITAB output presents a multiple regression equatior =b0+b1x1+b2x2+b3x3+b4x4
The regression equation is
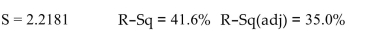
Let be the coefficient Test the hypothesis rersus
level. What do you conclude?
Definitions:
Product Placement
The practice of intentionally placing products in movies, shows, or other media content for promotional purposes.
Promotional Deal
An offer designed to stimulate purchases through special discounts, coupons, or other incentives.
Mass Media Buy
The purchase of advertising space or time on widely distributed media platforms to reach a large audience.
Loyalty Program
A rewards program offered by a company to customers who frequently make purchases, encouraging continued business by offering benefits or perks.
Q20: An environmental scientist obtains a sample of
Q29: Samples were drawn from three populations.
Q29: If a firm's goal is to maximize
Q29: Characterize the relationship shown in the figure.
Q33: Last year Altman Corp. had $205,000 of
Q34: The arrow on the spinner shown below
Q37: There are three primary disadvantages of a
Q53: Companies generate income from their "regular" operations
Q64: Suppose you are the president of a
Q76: Which of the following statements is CORRECT?<br>A)