The temperature of an oven remains constant at 379 degrees Fahrenheit. A potato is placed in the oven to bake. The difference between the temperature of the oven and that of the potato after 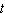 mi-
mi-
Nutes in the oven is given by degrees Fahrenheit. Write a formula that gives the tempera-
Ture , in degrees Fahrenheit, of the potato after 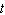 minutes in the oven.
minutes in the oven.
Definitions:
Primary Mycelium
A mycelium in which the cells are monokaryotic and haploid; a mycelium that grows from either an ascospore or a basidiospore. Compare with secondary mycelium.
Basidiomycetes
A class of fungi characterized by producing spores on club-shaped structures called basidia, including mushrooms, toadstools, and puffballs.
Dikaryotic
Describing a fungal cell or mycelium with two genetically distinct nuclei per cell, typically found in the life cycle of fungi.
Blastospores
A type of fungal spore produced by budding from a parent cell, common among yeast and other fungal organisms, serving as a means of asexual reproduction.
Q7: You put a drink in the freezer
Q8: Federal income taxes paid are deductible as
Q16: Which of the following is the
Q26: Solve the equation <span class="ql-formula"
Q50: Hobby expenditures are deductible to the extent
Q54: The following table shows the number
Q58: Insurance policy dividends used to purchase additional
Q75: At the outside wall the roof is
Q78: Deductions for AGI are:<br>A) Always deductible<br>B) Deductible
Q98: Below is a graph of a