Forwarding logic design. For this problem you are to design a forwarding unit for a 5- stage pipeline processor. The forwarding unit returns the value to be forwarded to the current instruction. There are three places that the values for register RS and register RT can come from: decode stage (register file), memory stage, and write-back stage. 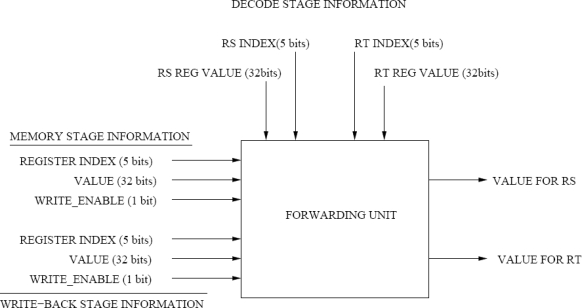 The write-back and memory stage information consists of: _INDEX- explaining which inflight register index is to be written _VALUE- the value that is to be written _ENABLE- whether or not the instruction in the stage is writing.
The write-back and memory stage information consists of: _INDEX- explaining which inflight register index is to be written _VALUE- the value that is to be written _ENABLE- whether or not the instruction in the stage is writing.
The decode stage simply states the register index (for RS and RT) and the corresponding register value from the register file.
Generally three values could exist, one of which the forwarding unit should choose for each of the RS and RT register value requests. The memory stage has value MEM, the write-back stage has value WB, and the register file has value RS-REG or RT-REG.
Using the table below which contains information about all of the instruction stages, indicate which value should be forwarded to the current instruction: MEM, WB, RS-REG, or RT-REG. Each line represents a Forwarding unit evaluation; there is no connection between evaluation lines in the table. You do not need to worry about hazard detection, only value bypassing.
Definitions:
Kohlberg
Lawrence Kohlberg was a developmental psychologist known for his theory of moral development, which outlines how individuals develop moral reasoning through a series of stages.
Moral Dilemmas
Situations in which a decision must be made between two or more morally conflicting options, with no clear right answer.
Social Comparisons
The process of evaluating oneself by comparing with others, often to assess one's abilities, status, or opinions.
Middle Childhood
A developmental stage covering roughly the ages of 6 to 12 years, characterized by significant growth in intellectual, physical, and social abilities.
Q2: Name the elements in the following
Q4: Describe hot spots in casting.
Q5: a.Suppose you need to store a list
Q6: Which of the following would be an
Q6: Level Three leadership refers to one's:<br>A) Genetic
Q11: Define brainstorming.
Q18: New experiments generate new _.
Q20: Consider the following assembly language code:<br>I0: ADD
Q28: Describe the general characteristics of a program
Q74: What is the purpose of boring?