You are given a 4-stage pipelined processor as described below.
IF: Instruction Fetch
IDE: Instruction Decode, Register Fetch, ALU evaluation, branch instructions change PC, address calculation for memory access.
MEM: memory access for load and store instructions.
WB: Write the execution result back to the register file. The writeback occurs at the 2nd half of the cycle.
Assume the delayed branching method discussed in Section 4.3. For the following program, assume that the loop will iterate 15 times. Assume that the pipeline finishes one instruction every cycle except when a branch is taken or when an interlock takes place. An interlock prevents instructions from being executed in the wrong sequence to preserve original data dependencies. Assume register bypass from both the IDE output and the MEM output. Also assume that r2 will not be needed after the execution returns.
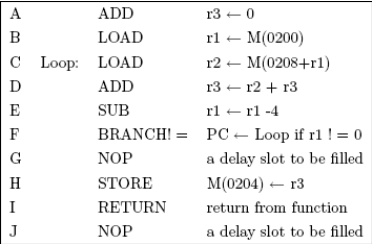 (a) Is there any interlock cycle in the program? If so, perform code reordering on the program and show the new program without interlock cycle.
(a) Is there any interlock cycle in the program? If so, perform code reordering on the program and show the new program without interlock cycle.
(b) Derive the total number of cycles required to execute all instructions before and after you eliminated the interlock cycle.
(c) Fill the delay slots. Describe the code reordering and/or duplication performed. Show the same program after delay slot filling. Recall that RETURN is also a branch instruction. Use a ' to mark the new copy of a duplicated instruction. For example, if you duplicated D, name the new copy D'.
(d)Derive the total number of cycles required to execute all instructions after you filled the delay slots.
Definitions:
Customer Order
A request made by a customer for a specific product or service from a business.
Mass Customization
Mass customization is a manufacturing and business strategy that combines the flexibility and personalization of custom-made products with the low unit costs associated with mass production.
Tailoring Products
The process of customizing goods or services to meet the specific needs or preferences of individual customers or market segments.
High-Volume Scale
Operations or production methods designed to handle large quantities of products or transactions efficiently.
Q1: Write a complete program that prints numbers
Q3: _ is to implement one method in
Q4: Name common roles that appear in new
Q4: It's important to focus on national differences
Q6: How many degrees of unsaturation are there
Q16: After the following program is finished, how
Q48: Which of the following molecules is achiral
Q55: Which of the following compounds are pairs
Q63: Based on the molecular formula C<sub>10</sub>H<sub>18</sub>
Q68: Identify the contents of the 200, 300,