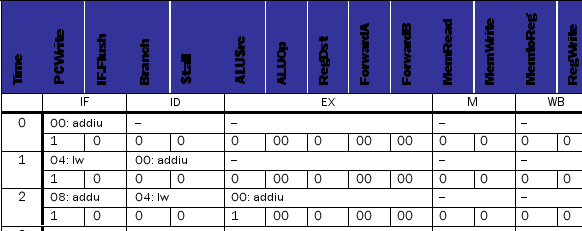
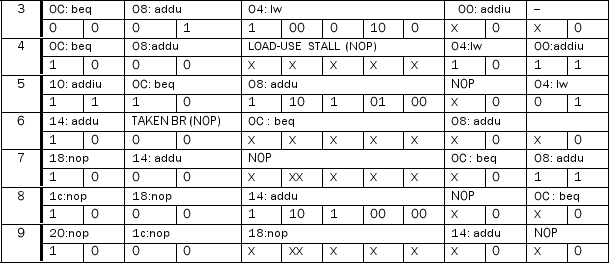
Consider the datapath below. This machine does not support code with branch delay slots. (It predicts not-taken with a 1-cycle penalty on taken branches.) For each control signal listed in the table below, determine its value at cycles 3 through 9, inclusive. Also, show the instruction occupying each stage of the pipeline in all cycles. (Assume the IF/ID write-enable line is set to the inverse of the Stall signal.)
The initial state of the machine is:
PC = 0
All pipeline registers contain 0s
All registers in the register file contain 0s. The data memory contains 0s in all locations The instruction memory contains:
00: addiu $3, $zero, 4 04: lw $4, 100($3)
08: addu $2, $4, $3
0C: beq $4, $zero, 0x14 10: addiu $3, $3, 1
14: addu $2, $2, $3
all other locations contain 0
Use data forwarding whenever possible. All mux inputs are numbered vertically from "top" to "bottom" starting at 0 as you look at the datapath in the proper landscape orientation. Also, the values for ALUOp are:
 Instruction formats:
Instruction formats: 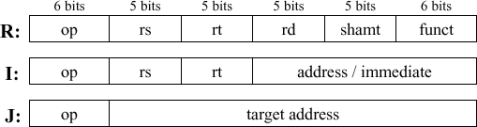
Definitions:
Analyze Consumer Data
The process of examining and interpreting data on customers' behaviors and preferences to make informed business decisions.
Geofencing
A location-based technology that creates a virtual boundary around a geographical area, triggering an action when a device enters or leaves that area.
Strip Mall
A type of shopping mall or plaza that is typically open-air and has a row of retail stores, services, or restaurants, usually accessible from a large parking area.
Coupons
Promotional tools used to offer discounts or rebates on products or services, aimed at increasing sales and customer loyalty.
Q1: The five stages described by L.E. Greiner
Q2: How many total SRAM bits will be
Q5: One of the most dangerous VABEs is:<br>A)
Q6: How many degrees of unsaturation are there
Q6: A competitive advantage has three characteristics: (fill
Q7: Strategic challenges occur at three levels, the:
Q17: Briefly describe dimensional constraints.
Q20: Describe upset forging.
Q22: Describe the function of parameter-driven assemblies and
Q45: Identify all stereogenic carbon atoms in the