Draw a mechanism for the following transformation.Include all necessary lone pairs of electrons,
curved arrows, and nonzero formal charges. 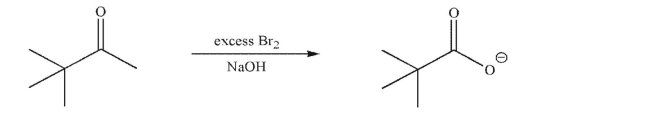
Definitions:
Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost is the loss of potential gain from other alternatives when one alternative is chosen.
Consumer Surplus
The separation between the total amount consumers are equipped and willing to pay for a good or service and what is effectively paid.
Total Surplus
The sum of consumer and producer surplus, reflecting the total benefit to society from the production and consumption of goods and services.
Consumer Surplus
The split between the maximum total consumers are prepared to pay for a product or service and the actual payment.
Q6: What is the product of the following
Q14: What is the product of the reaction
Q27: D-glucaric acid can also be named L-gularic
Q33: Provide the reagents necessary to achieve the
Q51: For each structure, state whether it is
Q54: Explain the difference in acidity between the
Q56: Predict the major organic product and provide
Q127: Which of the following is a
Q147: A researcher was interested in comparing
Q178: Determine whether the following statement regarding the