Canadian Accounting classifies accounts receivable as "current", "late", and "not collectible".
Industry figures show that 60% of A/R are current, 30% are late, and 10% are uncollectible. A law
firm in Markham Ontario has 500 accounts receivable: 320 are current, 100 are late and 80 are not
Collectible. Are these numbers in agreement with the industry distribution? 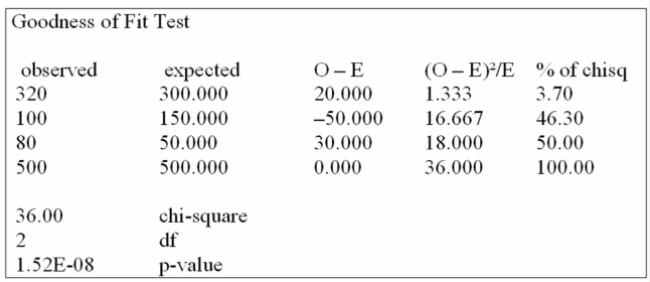
Using the data from this Megastat printout, you determine:
Definitions:
Distributive Bargaining
A negotiation strategy that focuses on dividing a fixed amount of resources or benefits among the parties involved, often resulting in a win-lose scenario.
Interdependent Situations
Refers to scenarios where the actions, decisions, or outcomes for one party are influenced or determined by those of another.
Lowball/Highball
Tactics in negotiation where one party intentionally makes a significantly lower or higher offer than expected, aiming to shift the bargaining range.
Hardball Tactics
Aggressive negotiation strategies focused on obtaining advantage by applying pressure or deceit.
Q1: (i. The mode is 21.<br>(ii. The arithmetic
Q11: i. The coefficient of correlation is a
Q22: i. One characteristic of the F distribution
Q29: You have a decision to invest $10,000
Q62: i. The chi-square goodness-of-fit test is appropriate
Q93: If the coefficient of multiple determination is
Q148: i. An outlier is a value in
Q157: What is the measure that indicates how
Q160: A sales manager for an advertising agency
Q199: (i. The research director of a large