(Exhibit: Saving, Investment, and the Interest Rate 1) 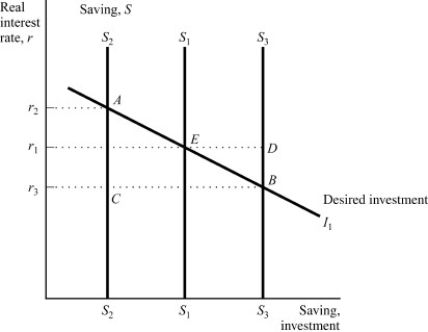 Reference: Ref 3-1
Reference: Ref 3-1  (Exhibit: Saving, Investment, and the Interest Rate 1) The economy begins in equilibrium at
(Exhibit: Saving, Investment, and the Interest Rate 1) The economy begins in equilibrium at
Point E, representing the real interest rate, r1 , at which saving, S1 , equals desired
Investment, I1 . What will be the new equilibrium combination of real interest rate, saving, and
Investment if the government cuts taxes, holding other factors constant?
Definitions:
Mutual Motivation
A concept where individuals or groups encourage each other to achieve goals, fostering a collaborative and supportive environment.
Coordinate Confrontation
A strategic approach to resolve conflict that involves organizing and managing a situation or dispute in a systematic way to find a solution.
Openness
A personality trait that involves the willingness to try new things, be open to new experiences, and entertain new ideas.
Distributive Negotiations
A negotiation strategy where the parties involved view the situation as a fixed pie, where any gain by one side is a loss to the other.
Q6: The decision by regulators during the S&L
Q26: If you call your broker and tell
Q62: The original purpose of savings institutions was
Q69: Your grandparents give you $1,000 as a
Q73: In a small open economy, starting from
Q73: If total investment (measured in billions of
Q94: An example of decreasing returns to scale
Q98: In a Cobb-Douglas production function the marginal
Q106: If the money supply increases 12 percent,
Q108: An economy's equals its .<br>A)consumption; income<br>B)consumption; expenditure