Suppose a country's population at any time t grows in accordance with the rule 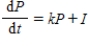 where P denotes the population at any time t, k is a positive constant reflecting the natural growth rate of the population, and I is a constant giving the (constant) rate of immigration into the country. The population of the United States in the year 1980
where P denotes the population at any time t, k is a positive constant reflecting the natural growth rate of the population, and I is a constant giving the (constant) rate of immigration into the country. The population of the United States in the year 1980  was 224.5 million. Suppose the natural growth rate is 0.8% annually
was 224.5 million. Suppose the natural growth rate is 0.8% annually 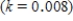 and net immigration is allowed at the rate of 0.5 million people/year
and net immigration is allowed at the rate of 0.5 million people/year 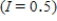 until the end of the century. What will be the U.S. population in 2003? Round the answer to the nearest tenth of a million, if necessary. P=__________ million
until the end of the century. What will be the U.S. population in 2003? Round the answer to the nearest tenth of a million, if necessary. P=__________ million
Definitions:
Deadweight Loss
A loss of economic efficiency that occurs when the equilibrium for a good or a service is not achieved or is unachievable.
Elastic
Describes a situation in which the demand or supply for a good or service significantly changes in response to a change in price.
Deadweight Loss
A loss of economic efficiency that occurs when the equilibrium outcome is not achieved due to market distortion, such as taxes or subsidies, leading to a reduction in total welfare.
Vacationing Abroad
The act of traveling to another country for leisure, exploration, or relaxation purposes.
Q5: Which of the following statements concerning the
Q7: Evaluate the following improper integral whenever it
Q8: Quinn's proprietorship earned $160,000 in pre-tax
Q25: The Country Workshop's total weekly profit (in
Q125: Find the indefinite integral.<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8255/.jpg" alt="Find
Q133: Find the indefinite integral. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8255/.jpg"
Q159: Determine whether the statement is true or
Q168: Evaluate the following improper integral whenever it
Q171: Evaluate the definite integral by using the
Q186: Evaluate the definite integral by using the