Two chemical solutions, one containing N molecules of chemical A and another containing M molecules of chemical B, are mixed together at time t = 0. The molecules from the two chemicals combine to form another chemical solution containing y (AB) molecules. The rate at which the AB molecules are formed, 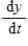 , is called the reaction rate and is jointly proportional to
, is called the reaction rate and is jointly proportional to 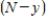 and
and 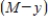 . Thus,
. Thus, 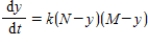 where k is a constant (we assume the temperature of the chemical mixture remains constant during the interaction). Solve this differential equation with the side condition
where k is a constant (we assume the temperature of the chemical mixture remains constant during the interaction). Solve this differential equation with the side condition 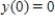 assuming that
assuming that 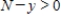 and
and 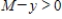
Definitions:
Wilhelm Wundt
Often considered the father of experimental psychology, he established the first psychology laboratory at the University of Leipzig, Germany.
Psychology Laboratory
A controlled environment where psychological research, experiments, and testing are conducted to study the human mind and behavior.
Sensations
The immediate and basic experiences generated from sensory stimulation, such as seeing or hearing.
Psychology
The scientific study of the mind and behavior, encompassing various aspects of conscious and unconscious experience as well as thought.
Q5: When a business being sold is no
Q8: Island Tours Inc.earned $80,000 in revenue and
Q10: Havana Pérez purchased a piece of land
Q12: Emily Spring sold the following items
Q27: Minimize the function <br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8255/.jpg" alt="Minimize
Q37: In using the trapezoidal rule, the number
Q59: Double jeopardy prevents individuals from being tried
Q63: Estimate the present value of an annuity
Q85: The concept of precedent emerged in the
Q162: Find the volume of the solid bounded