The volume V (in liters) of a certain mass of gas is related to its pressure P (in millimeters of mercury) and its temperature T (in degrees Kelvin) by the law 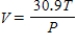
Compute 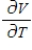 and
and 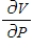 when T = 260 and P = 700.
when T = 260 and P = 700.
Definitions:
Unpleasant Stimuli
External or internal factors that are perceivable and can cause discomfort or negativity.
Aversive Stimuli
An unpleasant or harmful object, event, or situation that causes a decrease in the behavior it follows.
Behavior Modification
A technique aimed at changing behavior through systemic reinforcement or punishment.
Extinguish Misbehavior
The process of using behavioral modification techniques to reduce or eliminate undesired behaviors by removing the reinforcement that maintains the behavior.
Q2: There are several benefits to incorporating a
Q6: Jai Raines is the sole shareholder of
Q33: The demand function for a certain make
Q42: Assume that the rate of change of
Q51: Find the general solution of the first-order
Q72: Find the first partial derivatives of the
Q164: Find the critical point(s) of the function.
Q172: Let <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8255/.jpg" alt="Let .
Q192: Find the total differential of the function.
Q210: Sinclair wishes to supplement his retirement income