The population aged 65 years old and older (in millions) from 2000 to 2050 is projected to be 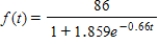
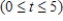
Where  is measured in decades, with
is measured in decades, with 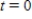 corresponding to 2000. What will be the average population aged 65 years and older over the years from 2000 to 2020? (Hint: The average population is given by
corresponding to 2000. What will be the average population aged 65 years and older over the years from 2000 to 2020? (Hint: The average population is given by 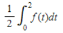 . Multiply the integrand by
. Multiply the integrand by 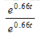 and then use the method of substitution.) Round your answer to one decimal place.
and then use the method of substitution.) Round your answer to one decimal place.
Definitions:
Future Cash Flows
Estimated monetary gains or expenditures that a company expects to receive or pay out in the future.
Straight-Line Depreciation
A method of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life in equal installments.
Mutually Exclusive
A statistical term describing two or more events that cannot occur simultaneously.
Salvage Value
The estimated residual value of an asset at the end of its useful life, important for depreciation calculations.
Q18: It is known that the quantity demanded
Q27: Minimize the function <br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8255/.jpg" alt="Minimize
Q32: Sketch the graphs of the given functions
Q42: Find <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8255/.jpg" alt="Find by
Q52: Find the derivative of the function.<br> <img
Q86: Simplify the expression.<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8255/.jpg" alt="Simplify the
Q87: Use the table of integrals to find
Q172: Find the indefinite integral.<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8255/.jpg" alt="Find
Q186: Minimize the function<br><br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8255/.jpg" alt="Minimize the
Q237: How long will it take an investment