The position of car A and car B, starting out side by side and traveling along a straight road, is given by s = f(t) and s = g(t) , respectively, where s is measured in feet and t is measured in seconds (see the accompanying figure) . 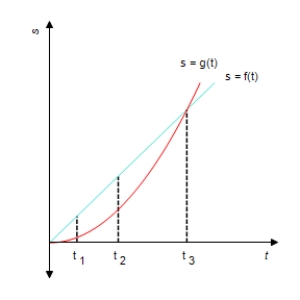
Which car is traveling faster at t1, t2 and t3?
Definitions:
Rate-Limiting Step
The slowest step in a chemical reaction sequence which determines the overall reaction rate.
Reaction-Energy Diagram
A reaction-energy diagram graphically shows the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction, from reactants to products, highlighting the activation energy and overall energy release or absorption.
Highest-Energy Structure
The conformation or arrangement of atoms in a molecule that has the highest potential energy, often least stable, compared to other conformations.
Molecular Collision
The process in which two or more particles (atoms, ions, molecules) come into close enough proximity to affect each other's trajectories or engage in a chemical reaction.
Q8: Find the slope and an equation of
Q25: Find the absolute maximum value and the
Q77: Use the fact that the <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8255/.jpg"
Q100: Let <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8255/.jpg" alt="Let .
Q118: Simplify the expression.<br><img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8255/.jpg" alt="Simplify the expression.
Q121: Determine whether the statement is true or
Q133: If f and g are functions, then
Q266: A study prepared for the National Association
Q272: The volume of a right-circular cylinder of
Q295: Find the derivative of the function.