Use the Newton method to approximate the indicated zero of the function. Continue with the iteration until two successive approximations differ by less than 0.0001. Round your answer to five decimal places, if necessary.
The zero of 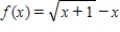 between
between 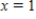 and
and 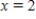 ,
,  .
.
Definitions:
Unlawful Distributions
Refers to the illegal dispensation, sharing, or allocation of assets or resources, often seen within the context of corporations or trust laws.
Director Liability
The legal responsibility of corporate directors for actions or omissions that cause harm to the company or its shareholders.
Unlawful Distributions
Financial distributions made by a company to its shareholders that violate laws or the company's own regulations, potentially harming the company or its creditors.
Usurped Corporate Opportunity
An act where an individual takes advantage of an opportunity that rightfully belongs to a corporation, typically violating fiduciary duties.
Q1: What factors increase the risk of vehicular
Q4: An 85-year-old man accompanied by his son
Q5: The home health nurse periodically interviews patients
Q8: The nurse clarifies that the biologic theory
Q10: The nurse cautions the Certified Nursing Assistants
Q11: Find the equation of the tangent line
Q13: Find the derivative of the function.<br> <img
Q14: Rationalize the numerator of the expression. ��
Q24: What does the presence of a caregiver
Q34: Find the Taylor series of the function