TABLE 14-11
A weight-loss clinic wants to use regression analysis to build a model for weight-loss of a client (measured in pounds) . Two variables thought to affect weight-loss are client's length of time on the weight-loss program and time of session. These variables are described below:
Y = Weight-loss (in pounds)
X₁ = Length of time in weight-loss program (in months)
X₂ = 1 if morning session, 0 if not
X₃ = 1 if afternoon session, 0 if not (Base level = evening session)
Data for 12 clients on a weight-loss program at the clinic were collected and used to fit the interaction model:
Y = β₀ + β₁X₁ + β₂X₂ + β₃X₃ + β₄X₁X₂ + β₅X₁X₂ + ε
Partial output from Microsoft Excel follows:
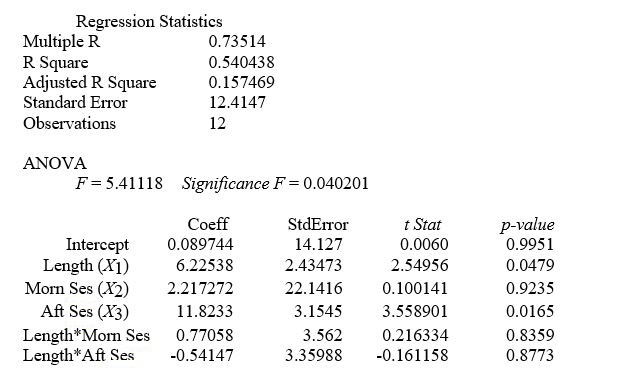
-Referring to Table 14-11, what null hypothesis would you test to determine whether the slope of the linear relationship between weight-loss (Y) and time in the program (X₁) varies according to time of session?
Definitions:
Scientific Management
A theory of management that analyzes and synthesizes workflows to improve economic efficiency, especially labor productivity, introduced by Frederick W. Taylor.
Bargaining Power
The capacity of one party to dominate negotiations due to their resources, status, or strategic position.
Collective Bargaining
The process whereby union representatives and employers negotiate labor contracts pertaining to wages, hours, benefits, and working conditions.
Perfectly Competitive
A market structure characterized by many buyers and sellers, no barriers to entry or exit, and where all firms sell identical products, leading to price determination purely by supply and demand.
Q11: Referring to Table 13-4, _ % of
Q37: If you wanted to find out if
Q44: Referring to Table 15-5, what is the
Q66: Referring to Table 15-3, suppose the chemist
Q75: Data that exhibit an autocorrelation effect violate
Q86: Referring to Table 13-12, what percentage of
Q92: Referring to Table 12-12, if the null
Q96: If the Durbin-Watson statistic has a value
Q194: Referring to Table 14-17 Model 1, the
Q231: Referring to Table 14-3, to test for