TABLE 15-1
A certain type of rare gem serves as a status symbol for many of its owners. In theory, for low prices, the demand increases and it decreases as the price of the gem increases. However, experts hypothesize that when the gem is valued at very high prices, the demand increases with price due to the status owners believe they gain in obtaining the gem. Thus, the model proposed to best explain the demand for the gem by its price is the quadratic model:
Y = β₀ + β₁X + β₁X² + ε
where Y = demand (in thousands) and X = retail price per carat.
This model was fit to data collected for a sample of 12 rare gems of this type. A portion of the computer analysis obtained from Microsoft Excel is shown below: 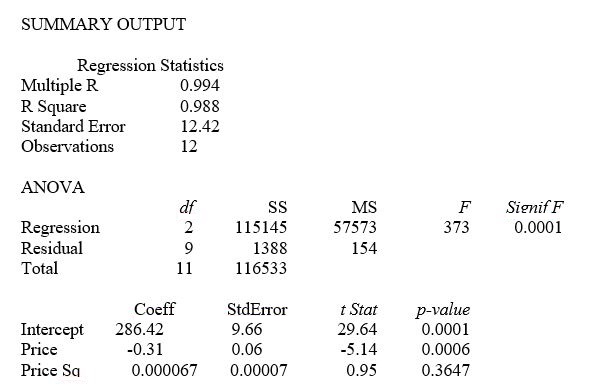
-Referring to Table 15-1, what is the correct interpretation of the coefficient of multiple determination?
Definitions:
Forward Contract
A non-standardized contract between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specified future time at a price agreed upon today.
Cash Flow Hedge
A strategy used in financial risk management to protect against the risk associated with fluctuations in cash flows due to changes in interest rates, foreign exchange rates, or other variables.
Initiation Date
The specific date at which a particular transaction, project, or contract begins.
Forward Contract
A bespoke contract involving two parties for the buying or selling of an asset at an agreed price on a designated future date.
Q16: The stepwise regression approach takes into consideration
Q25: Referring to Table 17-2, what is the
Q26: Referring to Table 14-19, what should be
Q41: Referring to 14-16, what is the correct
Q52: Referring to Table 13-9, the degrees of
Q64: If a new machine of a production
Q134: Referring to Table 14-5, what is the
Q151: Referring to Table 13-11, what are the
Q273: In a particular model, the sum of
Q309: Referring to Table 14-4, the observed value