To determine the break-even point, or the number of units that must be sold so that no profit or loss occurs, an economist uses the formula 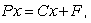 where P is the selling price per unit, x is the number of units that must be sold to break even, C is the cost to make each unit, and F is the fixed cost. A business analyst has determined that the selling price for a laser printer is $1800. The cost to make one laser printer is $960, and the fixed cost is $289,800.
where P is the selling price per unit, x is the number of units that must be sold to break even, C is the cost to make each unit, and F is the fixed cost. A business analyst has determined that the selling price for a laser printer is $1800. The cost to make one laser printer is $960, and the fixed cost is $289,800.
Find the break-even point.
Definitions:
Cost of Capital
The rate of return that a company must earn on its investment projects to maintain its market value and satisfy its investors.
Leveraged Value
Utilizing a range of financial tools or leveraging debt to amplify the possible gains from an investment.
Capital Structures
The mix of a company's long-term debt, specific short-term debt, common equity, and preferred equity, constituting how a firm finances its overall operations and growth.
Tax Shelters
Investment strategies or financial arrangements used to minimize tax liabilities, often by deferring or reducing taxable income.
Q3: Write the logarithm in expanded form. <img
Q16: The square of a positive number is
Q20: Solve by substitution: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8311/.jpg" alt="Solve by
Q23: Write <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8311/.jpg" alt="Write %
Q29: Let <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8311/.jpg" alt="Let Find:
Q43: Solve by taking square roots: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8311/.jpg"
Q50: Given <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8311/.jpg" alt="Given =
Q60: Write the number <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8311/.jpg" alt="Write the
Q101: Factor: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8311/.jpg" alt="Factor: A)
Q155: Multiply: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8311/.jpg" alt="Multiply: A)