The next few questions refer to the following evolutionary tree, whose horizontal axis represents time (present time is on the far right) and whose vertical axis represents morphological change.
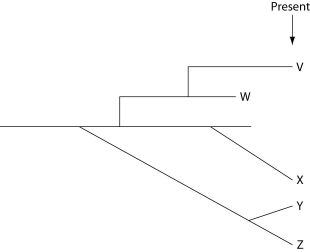
-Which conclusion can be drawn from this evolutionary tree?
Definitions:
Androgen-Binding Protein
A protein that binds to androgens (male sex hormones), facilitating their transport and function within the body.
Meiosis
A type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, creating four haploid cells, each genetically distinct from the parent cell, as seen in the production of gametes and plant spores.
Gametes
Sex cells (sperm and eggs) that carry genetic information for reproduction.
Chromosome Number
The total number of chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell, which varies among different organisms and is characteristic of each species.
Q16: Which of the following reduces gene flow
Q26: Approximately how far back in time does
Q28: Gymnosperms differ from both extinct and extant
Q31: What is the most probable explanation for
Q41: Which two processes are responsible for the
Q59: Rank the following one-base point mutations (from
Q66: Biologists have long been aware that the
Q67: Mycoplasmas are bacteria that lack cell walls.
Q68: What is the estimated frequency of allele
Q97: The seed coat's most important function is