The next questions refer to the following table, which compares the % sequence homology of four different parts (two introns and two exons) of a gene that is found in five different eukaryotic species. Each part is numbered to indicate its distance from the promoter (e.g., Intron I is the one closest to the promoter) . The data reported for species A were obtained by comparing DNA from one member of species A to another member of species A.
% Sequence Homology
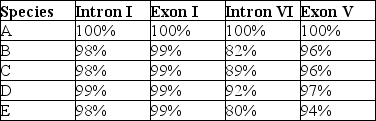
-Which of these four gene parts should allow the construction of the most accurate phylogenetic tree, assuming that this is the only part of the gene that has acted as a reliable molecular clock?
Definitions:
F-Test Statistic
A type of statistical test used to compare the variances of two populations or to test the significance of regression coefficients in a linear regression model.
Sum Of Squares
A statistical technique used to measure the variation or deviation of a set of values from the mean of those values.
Multiple Regression
A statistical technique that models and analyzes the relationship between a single dependent variable and two or more independent variables.
Coefficient Of Determination
A statistical measure that quantifies the proportion of the variance in the dependent variable predictable from the independent variable(s).
Q12: Which of the following represents the true
Q17: Which two species might be expected to
Q20: The reason that paralogous genes can diverge
Q41: Which section of sea-floor crust should have
Q43: The larvae of some insects are merely
Q46: Which of the following should have had
Q55: One possible use of transgenic plants is
Q56: In animal cells and in the meristem
Q60: A fungal spore germinates, giving rise to
Q65: Swine are vulnerable to infection by bird