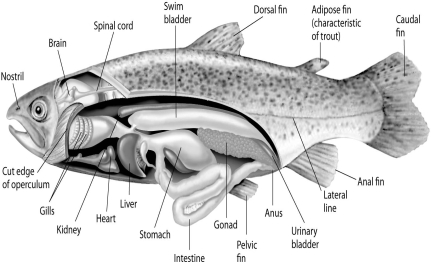
Figure 34.1
Fishes that have swim bladders can regulate their density and, thus, their buoyancy. There are two types of swim bladder: physostomus and physoclistus. The ancestral version is the physostomus version, in which the swim bladder is connected to the esophagus via a short tube (Figure 34.1) . The fish fills this version by swimming to the surface, taking gulps of air, and directing them into the swim bladder. Air is removed from this version by "belching." The physoclistus version is more derived, and has lost its connection to the esophagus. Instead, gas enters and leaves the swim bladder via special circulatory mechanisms within the wall of the swim bladder.
-The presence of a swim bladder allows the typical ray-finned fish to stop swimming and still
Definitions:
Utility-Maximizing
The economic principle that individuals or firms seek to get the greatest satisfaction or profit from their resource choices.
Utility
The satisfaction or benefit derived from consuming goods or services.
Consumer Wants
Desires or needs that individuals seek to satisfy through the purchase of goods or services.
Total Utility
The overall satisfaction or value a consumer receives from consuming a given quantity of a good or service.
Q3: Increasing the number of stomata per unit
Q7: Why might animal hormones function differently than
Q8: The ancestors of land plants were aquatic
Q15: All fungi share which of the following
Q17: Suppose an efficient conducting system evolved in
Q23: The nematocysts of sea slugs should be
Q37: Chemicals, secreted by soil fungi, that inhibit
Q45: What is true of charophytes?<br>A) They are
Q52: Plants that have their flowering inhibited by
Q83: In most fungi, karyogamy does not immediately