A particle starts from the origin at t = 0 with a velocity of (16 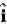 − 12
− 12  ) m/s and moves in the xy plane with a constant acceleration of
) m/s and moves in the xy plane with a constant acceleration of 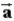 = (3.0
= (3.0 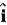 − 6.0
− 6.0  ) m/s2. What is the speed of the particle at t = 2.0 s?
) m/s2. What is the speed of the particle at t = 2.0 s?
Definitions:
Acetic Acid
A clear, colorless liquid with a strong vinegar odor, widely used as a solvent and chemical reagent, particularly in the production of vinyl acetate monomer and acetic anhydride.
Cyclohexanol
A cyclic alcohol with the formula C6H11OH, characterized by a six-membered ring with a single hydroxyl group attached.
Williamson Ether Synthesis
A method for preparing ethers by reacting an alkyl halide with an alkoxide ion, a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry to form ether bonds.
Ether
Organic compounds that are defined by having an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups.
Q1: Assume you are managing one of the
Q3: A spaceship leaves Earth and maintains a
Q7: The diagram below shows 3 vectors which
Q11: Three particles are placed in the xy
Q20: If vector <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8245/.jpg" alt="If vector
Q31: In what quadrant are both the sine
Q38: Sally, who weighs 450 N, stands on
Q48: A 2.0-kg block slides down a frictionless
Q58: A steel ball bearing of mass m<sub>1</sub>
Q79: Which of the following quantities is directly