If R = 2.0 kΩ, C = 4.0 mF, ε = 8.0 V, Q = 20 mC, and I = 3.0 mA, what is the potential difference Vb − Va? 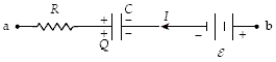
Definitions:
Constant Growth DCF Model
A method of valuing a company using the theory that its stock is worth the sum of all its future cash flows, discounted back to their present value at a constant growth rate.
Perpetual Preferred Stock
A type of preferred stock with no fixed maturity date, where dividends must be paid by the company before dividends are paid to common stockholders.
Expected Return
The weighted average of all possible returns for an investment, with weights representing the probabilities of each outcome.
Required Return
The minimum gain investors expect from an investment, considering its risk level; synonymous with required rate of return.
Q2: At what rate is thermal energy being
Q2: A charge of 8.0 pC is distributed
Q6: The algebraic sum of the changes of
Q9: An object moving on the x axis
Q14: A primary current of 6.0 A exists
Q31: A square coil (length of side =
Q34: A 30-μF capacitor is charged to 40
Q35: Two charges lie on the x axis,
Q36: If a = 60 cm, b =
Q40: The nucleus of lead-208, <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8245/.jpg" alt="The