Three 2.50 μC charges are placed on tiny conducting spheres at the ends of 1.00 m-long strings that are connected at 120° angles as shown below. The magnitude, in N, of the force on the knot at the center is 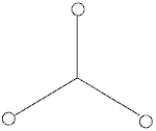
Definitions:
Electron-Pair Acceptor
A chemical entity that readily accepts a pair of electrons from another species to form a covalent bond, also known as a Lewis acid.
Proton Acceptor
A substance that can receive or take up protons (H+ ions), playing a critical role in acid-base reactions.
Curved Arrow Formalism
Curved arrow formalism is a notational system used in organic chemistry to depict the movement of electron pairs during chemical reactions, indicating bond formation and breakage.
Electron Pairs
Refers to two electrons occupying the same orbital in an atom or molecule, usually forming a covalent bond or participating in lone pairs.
Q7: Refer to Exhibit 15-1. The point at
Q17: If C<sub>P</sub> for an ideal gas is
Q17: Suppose that you were selected for a
Q32: Which of the following is not a
Q36: In an inertia balance, a body supported
Q47: The circuit below contains three 100-W light
Q53: If a = 60 cm, b =
Q63: An organ pipe open at both ends
Q76: Transverse waves are traveling on a 1.00-m
Q96: Points A [at (3, 6) m] and