Hooke's law: Block A (0.40 kg) and block B (0.30 kg) are on a frictionless table (see figure) . Spring 1 connects block A to a frictionless peg at 0 and spring 2 connects block A and block B. When the blocks are in uniform circular motion about 0, the springs have lengths of 0.60 m and 0.40 m, as shown. The springs are ideal and massless, and the linear speed of block B is 2.0 m/s. If the distance that spring 2 stretches is 0.060 m, the spring constant of spring 2 is closest to 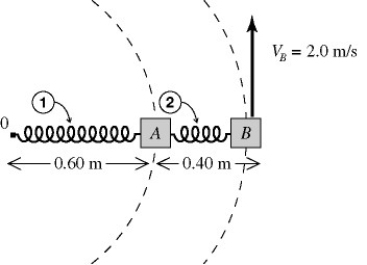
Definitions:
Employee Benefits
Various non-wage compensations provided to employees in addition to their normal wages or salaries, such as health insurance, paid vacations, and retirement plans.
Promotion Criteria
The standards and requirements that an employee must meet or exceed to be considered for advancement within an organization.
Chief Executive Officer
The highest-ranking executive in a company, responsible for making major corporate decisions, managing overall operations, and communicating with the board of directors.
Vice-president
An executive position in a company or organization whose holder is typically responsible for a specific department or group within the organization.
Q15: Slanted surfaces with friction: In the figure,
Q23: Sideropenic dysphagia is also known as Plummer-Vinson
Q25: Nine-mile fever is reported with code _.
Q47: Elastic collisions in one dimension: A 620-g
Q51: Energy conservation with conservative forces: In the
Q55: Newton's second law: On a horizontal frictionless
Q70: Rotational dynamics about a moving axis: A
Q88: Energy conservation with conservative forces: A 2.0-kg
Q92: Work: In the figure, a 700-kg crate
Q123: Multiple-object systems without friction: Two objects are