Two-dimensional motion: Object A has a position as a function of time given by 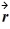 A(t) = (3.00 m/s) t
A(t) = (3.00 m/s) t  + (1.00 m/s2) t2
+ (1.00 m/s2) t2
 . Object B has a position as a function of time given by
. Object B has a position as a function of time given by 
B(t) = (4.00 m/s) t  + (-1.00 m/s2) t2
+ (-1.00 m/s2) t2
 . All quantities are SI units. What is the distance between object A and object B at time
. All quantities are SI units. What is the distance between object A and object B at time 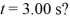
Definitions:
Audit Trail
A record that traces the detailed financial transactions of an entity to its original source for verification purposes.
Trade Record
Documentation or data that keeps track of all trading activities, including purchases and sales of securities.
Paper Trail
A series of documents or records that provide evidence of a person's or organization's transactions, actions, or history.
Expected Returns
The anticipated amount of profit or loss an investment is predicted to generate based on historical or projected performance.
Q6: Slanted surfaces with friction: A 200 g
Q11: Rolling: A solid sphere, solid cylinder, and
Q20: Cosmology: Dark matter was initially proposed to
Q22: Newton's second law: A block is on
Q48: Quantum numbers: If the principal quantum number
Q50: Inelastic collisions in one dimension: Two objects
Q51: Free fall: Two objects are dropped from
Q55: Basic kinematics variables: The figure represents the
Q70: Matter waves: In a double slit experiment,
Q77: Uncertainty principle using ΔEΔt ≥ ħ/2: An