Radioactivity: The stability of 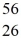 Fe with respect to alpha, β+, and β- decay is to be determined. Do not consider the possibility of decay by electron capture. The following atomic masses are known:
Fe with respect to alpha, β+, and β- decay is to be determined. Do not consider the possibility of decay by electron capture. The following atomic masses are known: 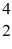 He: 4.002603 u
He: 4.002603 u 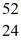 Cr: 51.944768 u
Cr: 51.944768 u 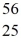 Mn: 55.938907 u
Mn: 55.938907 u 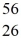 Fe: 55.934939 u
Fe: 55.934939 u 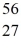 Co: 55.939841 u The
Co: 55.939841 u The 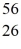 Fe nuclide is
Fe nuclide is
Definitions:
Nitrogen Cycle
A biogeochemical cycle describing the transformations of nitrogen and nitrogen-containing compounds in nature.
Slash-And-Burn Agriculture
A method of agriculture where vegetation is cut down and burned as a technique to clear land for cultivation, but can lead to soil degradation and deforestation.
Stratospheric Ozone
A layer of ozone molecules located in the Earth's stratosphere, protecting life by absorbing most of the sun's harmful ultraviolet radiation.
UVB
Ultraviolet B light, a component of sunlight with wavelengths between 280-315 nm, known for its role in vitamin D synthesis and skin tanning.
Q19: Work: A force <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8274/.jpg" alt="Work: A
Q25: Angular momentum: The magnitude of the orbital
Q27: Particle in a box: A 10.0-g bouncy
Q31: Free fall: At the same moment from
Q33: Zeeman effect: The energy of an electron
Q40: Multielectron atoms: The only VALID electron state
Q40: Elastic collisions in two dimensions: A pool
Q45: Uncertainty principle using ΔpΔx ≥ h/2: A
Q52: Basic kinematics variables: An object starts its
Q86: Equilibrium: A stepladder consists of two halves,