Basic kinematics variables: The figure shows the position of an object as a function of time, with all numbers accurate to two significant figures. Between time t = 0.0 s and time t = 9.0 s
(a) what is the average speed of the object?
(b) what is the average velocity of the object? 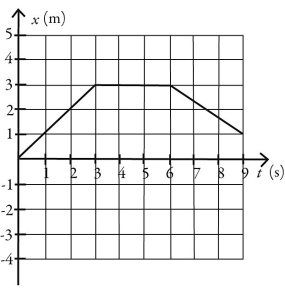
Definitions:
Sum Of Squared Residuals
The total value obtained by squaring each of the residuals (differences between observed and predicted values) and summing them all, commonly used in regression analysis.
Coefficient Of Determination
A measure, often represented as R^2, that indicates the proportion of the variance in the dependent variable predictable from the independent variable(s).
Linear Relationship
A relationship between two variables where the change in one variable is directly proportional to the change in another variable.
Error Variable
The error variable represents the component of randomness or unexplained variance in a statistical model, distinguishing between the observed and predicted values.
Q3: Single-slit diffraction: A light beam shines through
Q19: Cosmology: The cosmic background radiation corresponds to
Q22: Hubble's law: Estimate the speed of a
Q26: Quantum numbers: In the ground state, the
Q30: Radioactive decay: <sub>An isotope of Tc having
Q36: Self-inductance: In the figure, the current in
Q42: Matter waves: A nonrelativistic electron is accelerated
Q53: Eyes: The near point of a person's
Q72: Field due to a long wire: A
Q104: Slanted surfaces with friction: A 200 g