Faraday's law: A closed loop conductor that forms a circle with a radius of  is located in a uniform but changing magnetic field. If the maximum emf induced in the loop is
is located in a uniform but changing magnetic field. If the maximum emf induced in the loop is 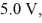 what is the maximum rate at which the magnetic field strength is changing if the magnetic field is oriented perpendicular to the plane in which the loop lies?
what is the maximum rate at which the magnetic field strength is changing if the magnetic field is oriented perpendicular to the plane in which the loop lies?
Definitions:
LMX Theory
Leadership Member Exchange theory focuses on the nature of the relationship between a leader and their followers, suggesting that leaders form unique bonds with each member, which can affect team dynamics and performance.
LMX Theory
Stands for Leader-Member Exchange theory, highlighting the distinct and unique relationships leaders form with each of their followers, which can lead to varying levels of job satisfaction and performance outcomes.
Negotiated Role
A role in a team or organization that is defined through the process of negotiation rather than assigned by hierarchy or tradition, often allowing for more flexible adaptation to changing needs.
LMX Theory
Leader-Member Exchange theory, suggesting that leaders develop unique one-to-one relationships with each of the people reporting to them.
Q6: Parallel plates: Two flat 4.0 cm ×
Q7: Lenz's law: In the figure, a copper
Q9: Lenz's law: In the figure, two solenoids
Q27: Electric field of multiple point-charges: Four equal
Q40: Flux: A nonuniform electric field is directed
Q45: Lens-maker's formula: A convex-concave thin lens is
Q48: Kirchhoff's rules: A multiloop circuit is shown
Q53: RC circuits: For the circuit shown in
Q65: Thin films: A soap bubble, when illuminated
Q69: Solenoids: A solenoid is wound with 970