LR circuits: For the circuit shown in the figure, the inductors have no appreciable resistance and the switch has been open for a very long time. 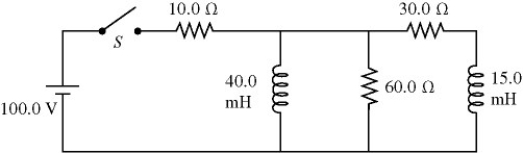 (a) The instant after closing the switch, what is the current through the 60.0-Ω resistor?
(a) The instant after closing the switch, what is the current through the 60.0-Ω resistor?
(b) The instant after closing the switch, what is the potential difference across the 15.0-mH inductor?
(c) After the switch has been closed and left closed for a very long time, what is the potential drop across the 60.0-Ω resistor?
Definitions:
Absorption Costing
In this accounting method, total costs of manufacturing, from direct materials and labor to both fixed and variable overheads, are completely absorbed into the product’s final cost.
Variable Costing
Variable costing is a cost accounting method that includes only variable production costs—direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead—in product cost calculations, excluding fixed overhead costs.
Production Costs
Expenses directly related to the creation of goods and services, including materials, labor, and overhead costs.
Fixed Production Costs
Costs that do not change with the level of production, such as rent, insurance, and salaries.
Q4: Electric field of a single point-charge: An
Q7: Total energy: How fast must a proton
Q31: Sheets of charge: A very large sheet
Q35: Quantity of heat: A thermally isolated system
Q35: Diffraction grating: Monochromatic light is incident on
Q36: Solenoids: A cylindrical insulated wire of diameter
Q36: Single-slit diffraction: A single-slit diffraction pattern is
Q39: Free fall: A rocket takes off vertically
Q52: Basic kinematics variables: An object starts its
Q95: Lens-maker's formula: In the figure, the radius