LR circuits: Consider the circuit shown in the figure. The battery has emf ε = 25 volts and negligible internal resistance. The inductance is 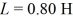 and the resistances are R1 = 12 Ω and R2 = 9.0 Ω. Initially the switch S is open and no currents flow. Then the switch is closed.
and the resistances are R1 = 12 Ω and R2 = 9.0 Ω. Initially the switch S is open and no currents flow. Then the switch is closed. 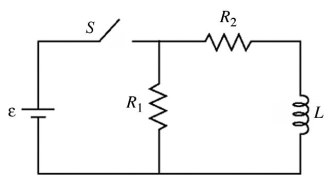 (a) What is the current in the resistor R1 just after the switch is closed?
(a) What is the current in the resistor R1 just after the switch is closed?
(b) After leaving the switch closed for a very long time, it is opened again. Just after it is opened, what is the current in R1?
Definitions:
Stockholder Wealth
The total value of a shareholder’s equity in a company, representing the shareholder's ownership interest.
Common Share
Equity ownership in a corporation, giving holders voting rights and a share in the company's profits through dividends.
MVA
Market Value Added, a calculation that shows the difference between the market value of a company and the capital contributed by investors.
Straight-line Basis
A method of calculating depreciation and amortization by allocating an equal amount of expense over each period of the asset's useful life.
Q4: Kinetic energy: How much work must be
Q8: Field intensity: Near the earth the intensity
Q14: Charge on conductors: An irregular conductor carries
Q17: Double-slit interference: In a double slit experiment,
Q30: Thin lenses: An object is placed 100
Q32: Internal battery resistance: When a 100-Ω resistor
Q36: Gauss's law: A nonuniform electric field is
Q48: Velocity selector: A beam of electrons is
Q51: Ohm's law: When a voltage difference is
Q54: AC generator: Suppose that you wish to