Potential energy of point-charges: A tiny object carrying a charge of + 3.00 μC and a second tiny charged object are initially very far apart. If it takes 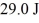 of work to bring them to a final configuration in which the
of work to bring them to a final configuration in which the 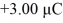 object i is at x = 1.00 mm, y = 1.00 mm, and the other charged object is at x = 1.00 mm, y = 3.00 mm, find the magnitude of the charge on the second object. (k = 1/4πε0 = 8.99 × 109 N ∙ m2/C2)
object i is at x = 1.00 mm, y = 1.00 mm, and the other charged object is at x = 1.00 mm, y = 3.00 mm, find the magnitude of the charge on the second object. (k = 1/4πε0 = 8.99 × 109 N ∙ m2/C2)
Definitions:
Equity Method
An accounting technique used to record investments in other companies, where the investment is initially recorded at cost and adjusted thereafter for the investor's share of the investee's net income or loss.
Patents
Intellectual property rights granted to an inventor, providing exclusive rights to use, sell, or manufacture the invention for a certain period.
Equipment
Tangible personal property used in operations, such as machinery or office hardware, that is not intended for sale.
Acquisition Differential
The difference between the cost of an acquisition and the fair value of net assets acquired, often recognized as goodwill on the balance sheet.
Q1: Spheres of charge: The graph in the
Q2: Poynting vector: The magnitude of the Poynting
Q4: Addition and subtraction: Vectors <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8274/.jpg" alt="Addition
Q12: Standing waves on a string: A wave
Q17: Flow rate: An incompressible fluid flows steadily
Q21: Standing sound waves: In a resonating pipe
Q52: Potential due to point-charges: Two positive point
Q52: Solenoids: A solenoid having N turns and
Q60: AC generator: Wire is wound on a
Q83: Force on moving charges: An electron, moving