Motion of a charged particle: A pair of charged conducting plates produces a uniform field of 12,000 N/C, directed to the right, between the plates. The separation of the plates is 40 mm. An electron is projected from plate A, directly toward plate B, with an initial velocity of vo = 2.0 × 107 m/s, as shown in the figure. (e = 1.60 × 10-19 C, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2, mel = 9.11 × 10-31 kg) The velocity of the electron as it strikes plate B is closest to 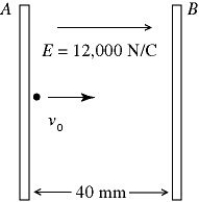
Definitions:
Phenotype Frequency
Phenotype frequency refers to the proportion of individuals in a population that exhibit a specific observable trait or phenotype.
Temporal Isolation
A prezygotic reproductive isolating mechanism in which genetic exchange is prevented between similar species because they reproduce at different times of the day, season, or year.
Genetic Exchange
The process by which genetic information is transferred between organisms, leading to variation in genetic makeup.
Diurnal Isolation
Diurnal isolation is a form of reproductive isolation where species may share the same habitat but are active at different times of the day, thus preventing mating.
Q2: Internal battery resistance: Two light bulbs, B<sub>1</sub>
Q4: Gravitational potential energy: An astronaut is standing
Q7: Field of a circular loop: A circular
Q8: Damped harmonic motion: A 2.15 kg lightly
Q15: RC circuits: A 4.0-μF capacitor that is
Q19: Molar heat capacities: An ideal monatomic gas
Q24: Potential energy of point-charges: Two point charges
Q30: Meters: A galvanometer with a resistance of
Q33: Mean free path: An ideal gas is
Q52: Kirchhoff's rules: A multiloop circuit is shown