Phase changes: A substance has a melting point of 20°C and a heat of fusion of 3.9 × 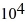 J/kg. The boiling point is
J/kg. The boiling point is 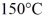 and the heat of vaporization is
and the heat of vaporization is 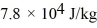 at a pressure of 1.0 atm. The specific heats for the solid, liquid, and gaseous phases are 600 J/(kg ∙ K) , 1000 J/(kg∙K) , and 400 J/(kg ∙ K) , respectively. The quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of
at a pressure of 1.0 atm. The specific heats for the solid, liquid, and gaseous phases are 600 J/(kg ∙ K) , 1000 J/(kg∙K) , and 400 J/(kg ∙ K) , respectively. The quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 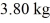 of the substance from
of the substance from 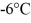 to
to 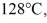 at a pressure of 1.0 atm, is closest to
at a pressure of 1.0 atm, is closest to
Definitions:
Foreign Portfolio Investment
Investment in financial assets from another country, such as stocks or bonds, without direct control over the businesses.
Trade Restrictions
Measures implemented by governments to control the amount of trade across its borders by limiting imports, exports, or both through mechanisms such as tariffs, quotas, and bans.
Labor Productivity
A measure of economic performance that calculates the efficiency of labor in producing goods and services.
Determinants Of Productivity
Factors affecting the efficiency of factor inputs in producing output, including technological advances, education, and infrastructure.
Q5: RC circuits: A 6.0-μF capacitor is connected
Q8: Energy in capacitors: A charge of 2.00
Q19: Resistors in combination: A resistor is made
Q32: Radiation: Betelgeuse is a red supergiant star
Q42: Energy in SHM: If we double only
Q44: Components: An airplane undergoes the following displacements:
Q54: Standing sound waves: A string 40.0 cm
Q87: Ampere's law: A long, straight wire with
Q101: Ideal gas law: A hot air balloon
Q121: Molecular speeds: What is the root-mean-square value